
This is typically provided as two separate 2.5-gram doses
A total of 5 grams is usually sufficient. 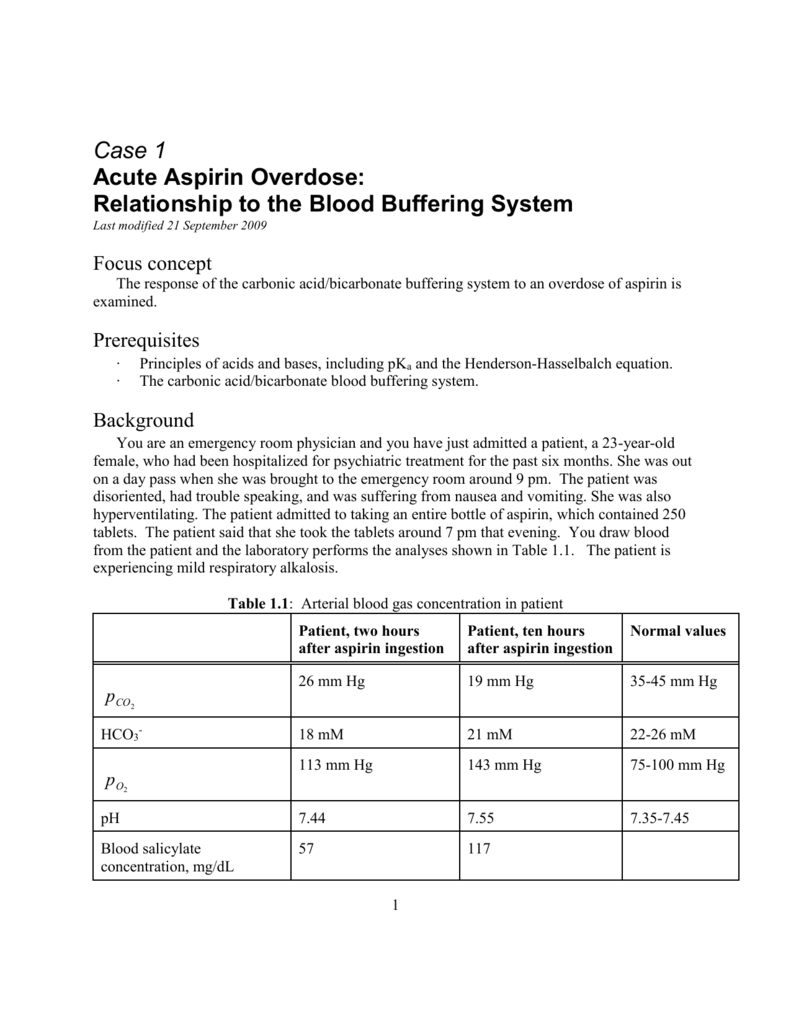
For most procedures (e.g., thoracentesis), an INR 25 seconds).
Note that pre-procedure INR correlates poorly with bleeding risk. Alternative: four units fresh frozen plasma. CNS bleed: consider traditional dosing:. Usually fixed dose PCC (1,500 Units), repeat INR in 30 minutes. 10 mg IV vitamin K over 30 minutes *plus* PCC or FFP. Anticoagulation reversal for minor procedures is generally unnecessary. There is little evidence that moderately elevated INR correlates with post-procedural bleeding after many procedures (e.g., ultrasound-guided central line placement or thoracentesis). Life-threatening bleeding requires aggressive normalization of coagulation parameters, but minor bleeding may respond to local measures. How important is it to reverse the anticoagulation? a mechanical mitral valve, which has a high risk of thrombosis). Some patients are anti-coagulated for higher risk conditions (e.g. Short-term interruption is generally fine. Most patients are anti-coagulated for atrial fibrillation or deep vein thrombosis. Why was the patient initially anti-coagulated? Determine what doses of medication the patient is on, and when is the last time a dose was taken. Review all medications the patient is taking which may affect coagulation (including over-the-counter aspirin or aspirin-containing products). In this situation, thromboelastography (TEG) may be more accurate.  For patients with cirrhosis or disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), traditional coagulation parameters (e.g., INR) don't necessarily reflect the true coagulation state.
For patients with cirrhosis or disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), traditional coagulation parameters (e.g., INR) don't necessarily reflect the true coagulation state. 
Consider all medications and coagulation labs in order to get a global sense of how coagulopathic the patient is.
Antidote for aspirin plus#
Critically ill patients often have several coagulopathies (e.g., thrombocytopenia plus supratherapeutic INR on warfarin). Pre-procedure coagulation management for common proceduresĬonsiderations when approaching anticoagulation reversal. Pharmacology of broad-spectrum reversal agents. Factor Xa inhibitors (riveroXABAN, apiXABAN, edoXABAN, fondaparinux).







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
